Effective Approaches to Lowering Breast Cancer Risk
Breast cancer represents a major health concern globally, with millions affected each year. While it is not possible to eliminate the risk of breast cancer entirely, adopting a combination of preventive strategies can significantly lower the likelihood of developing the disease. This guide provides a detailed overview of breast cancer, effective prevention methods, and practical advice for crafting a personalized approach to risk reduction.
Understanding Breast Cancer
Breast cancer begins when abnormal cells in breast tissue grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor that can potentially spread to other parts of the body if not caught early. The disease primarily manifests in several key types:
•Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC): This is the most common type of breast cancer. It starts in the milk ducts and invades nearby tissues, which may eventually spread to other areas if left untreated.
•Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC): ILC begins in the lobules, which are the milk-producing glands. This type is often harder to detect in its early stages compared to IDC.
•Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS): DCIS is a non-invasive form of cancer where abnormal cells are confined to the ducts of the breast. If not treated, DCIS can progress to invasive cancer.
Symptoms to Watch For:
•A New Lump or Mass: A new lump or mass in the breast or underarm area is one of the most common signs of breast cancer.
•Changes in Breast Size or Shape: Unexplained alterations in the size or shape of the breast should be evaluated.
•Unusual Nipple Discharge: Any discharge from the nipple that is not related to breastfeeding warrants a medical check-up.
Key Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Breast cancer risk is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetic, hormonal, and lifestyle components. Addressing these factors can help in reducing the risk of developing the disease:
Genetic Factors
•Genetic Testing: Inherited mutations in genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 can significantly increase the risk of breast cancer. For individuals with a family history of breast cancer, genetic testing is crucial. This testing can inform decisions about preventive measures and help in creating a tailored risk management strategy.
Hormonal Factors
•Hormonal Exposure: Long-term exposure to estrogen and progesterone, often due to factors like early menstruation, late menopause, or hormone replacement therapy, can elevate the risk of breast cancer. Understanding and managing hormonal exposure can be a key aspect of prevention.
Lifestyle Factors
•Diet: Maintaining a balanced diet that includes plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins, while reducing the intake of processed foods and limiting alcohol consumption, is beneficial for overall health and can lower breast cancer risk.
•Exercise: Regular physical activity is essential. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week. Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and improves overall well-being.
•Weight Management: Obesity is a known risk factor for breast cancer. Keeping a healthy weight through diet and exercise is an important preventive measure.
Effective Prevention Methods
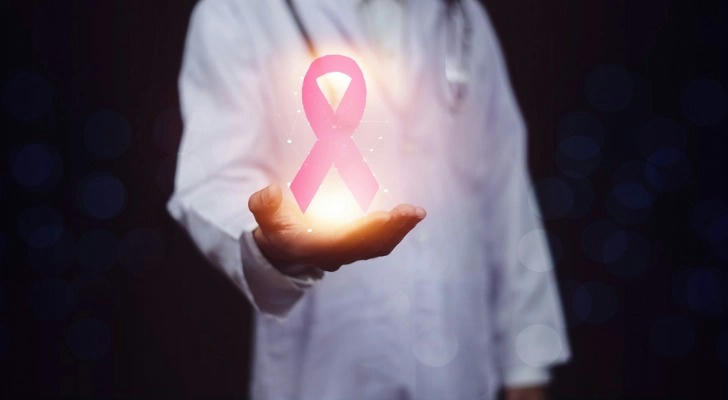

Implementing a combination of screenings, genetic assessments, and lifestyle changes can greatly reduce breast cancer risk:
Screenings
•Mammograms: Regular mammograms are vital for the early detection of breast cancer. Screening typically begins at age 45, but individual recommendations may vary based on personal risk factors. Follow your healthcare provider’s guidelines on screening frequency.
•Clinical Breast Exams: Regular clinical breast exams by healthcare professionals can aid in the early detection of abnormalities and should be a part of routine health care.
Genetic Testing and Preventive Measures
•Genetic Risk Assessment: For individuals with a family history of breast cancer or known genetic mutations, genetic testing can guide decisions about preventive measures such as prophylactic surgeries or chemoprevention.
Lifestyle Adjustments
•Healthy Eating and Exercise: Adopting a diet rich in nutrients and engaging in regular physical activity help maintain a healthy weight and reduce overall cancer risk.
•Weight Management: Regularly monitor and manage your weight to mitigate obesity-related risks.
Real-Life Success Stories
•Sophia's Approach: At age 40, Sophia learned she carried a BRCA2 mutation through genetic testing. Given her family history, she opted for a preventive mastectomy, which significantly lowered her risk and provided peace of mind.
•Mia's Experience: At 46, Mia, who did not have a family history but was overweight, made significant lifestyle changes, including improving her diet and increasing her physical activity. Regular screenings helped detect a small tumor early, underscoring the importance of lifestyle changes and consistent health monitoring.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Preventive strategies can come with their own set of challenges:
•Genetic Testing: While it provides valuable information, it may also induce anxiety about future health. Counseling can help manage these concerns.
•Preventive Surgeries: Procedures such as mastectomies can lead to physical and emotional changes. Support from counseling or support groups can be beneficial.
Creating a Personalized Prevention Plan
To effectively reduce breast cancer risk, consider the following steps:
1.Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized prevention plan based on your specific risk factors.
2.Set Manageable Goals: Implement realistic lifestyle changes and adhere to recommended screening schedules.
3.Embrace Healthy Habits: Focus on maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing weight.
4.Stay Proactive: Regular screenings and health check-ups are crucial for early detection and risk management.
5.Seek Support: Address any concerns or stress with professional counseling or support groups.
Conclusion
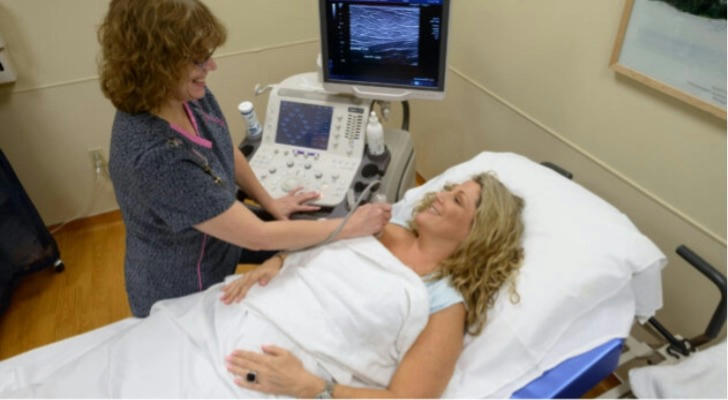
Although there is no guaranteed method to prevent breast cancer, combining regular screenings, genetic assessments, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can substantially lower the risk and enhance early detection. Creating a personalized prevention plan and seeking ongoing support are essential components of effective risk management and overall health maintenance.